[toc]
1, input子系统是用来解决输入问题的,所谓输入,即驱动为应用层提供数据。
2, 使用字符设备的read或者ioctl也可以实现输入操作,这种方式的弊端在于:驱动程序员自己定义数据格式,导致数据格式不统一,比如同样是按键输入,不同人实现的方式不一样,有人定义key=‘1’,有的人定义key=‘key1’。导致应用层程序调用驱动时传参不一致。此外,字符设备驱动框架提供数据的双向交流,input子系统只处理输入数据。
3, input子系统的好处: 为输入数据提供统一规范,驱动程序遵循填充该标准,应用程序遵循调用该标准。
4, 在文件系统中查看input设备
1
2
3
| myye@myye-vm:~$ ls /dev/input/event*
/dev/input/event0 /dev/input/event1 /dev/input/event2 /dev/input/event3 /dev/input/event4
myye@myye-vm:~$ sudo cat /dev/input/event0 # 查看键盘的事件,按下键盘按键,终端会打印相应的信息
|
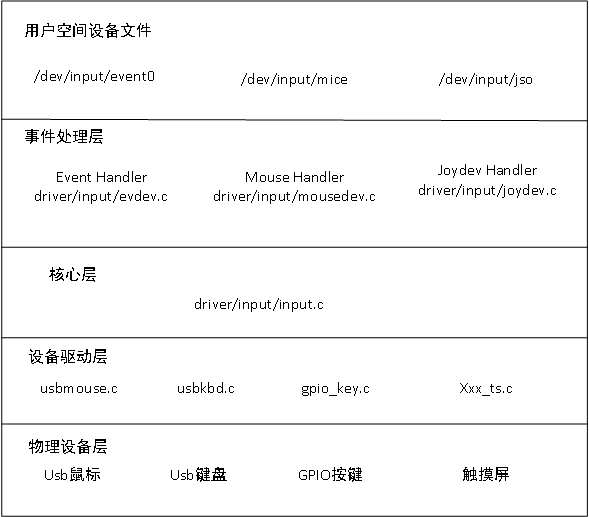
对于驱动开发来说,只需要实现 事件处理层和设备驱动层, 其中设备驱动层是关键,事件处理层内核也有通用事件处理的代码,可以更具需要进行修改。
相关头文件
1
| #include <linux/input.h>
|
核心数据结构
- 要遵循的规范结构
struct input_event - 驱动核心数据结构
struct input_dev , struct input_id
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| /* include/linux/input.h */
/*
* The event structure itself
*/
struct input_event {
struct timeval time; /* 事件产生的时间戳 */
__u16 type; /* 事件类型 */
__u16 code; /* 键码, 和type有关 */
__s32 value; /* 键值, 和code有关 */
};
|
此结构用于设备驱动上报事件
type
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /*
* Event types
*/
#define EV_SYN 0x00 /* 同步事件 */
#define EV_KEY 0x01 /* 按键事件 */
#define EV_REL 0x02 /* 相对事件 */
#define EV_ABS 0x03 /* 绝对事件 */
#define EV_MSC 0x04
#define EV_SW 0x05
#define EV_LED 0x11
#define EV_SND 0x12
#define EV_REP 0x14
#define EV_FF 0x15
#define EV_PWR 0x16
#define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17
#define EV_MAX 0x1f
#define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1)
|
每种输入设备,最后都必须有一个同步事件,按键事件指的是类似按钮或者键盘类的键值事件;绝对事件指的是产生的数据有最大值和最小值,比如重力传感器,陀螺仪之类的;相对事件指的是产生的数据是相对数值,比如鼠标产生的数据:下一个坐标是相对于之前的坐标的。
code
键码,数值与事件类型有关,如果是按键事件,键码就表示是哪一个按键;如果是绝对事件,键码就表示哪个坐标轴(ABS_X, ABS_Y)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| /* key类型code举例 */
#define KEY_RESERVED 0
#define KEY_ESC 1
#define KEY_1 2
#define KEY_2 3
#define KEY_3 4
#define KEY_4 5
#define KEY_5 6
#define KEY_6 7
#define KEY_7 8
#define KEY_8 9
#define KEY_9 10
#define KEY_0 11
#define KEY_MINUS 12
#define KEY_EQUAL 13
#define KEY_BACKSPACE 14
/* 相对事件类型code举例 */
/*
* Relative axes
*/
#define REL_X 0x00
#define REL_Y 0x01
#define REL_Z 0x02
#define REL_RX 0x03
#define REL_RY 0x04
#define REL_RZ 0x05
#define REL_HWHEEL 0x06
#define REL_DIAL 0x07
/* 绝对事件类型code举例 */
/*
* Absolute axes
*/
#define ABS_X 0x00
#define ABS_Y 0x01
#define ABS_Z 0x02
#define ABS_RX 0x03
#define ABS_RY 0x04
#define ABS_RZ 0x05
#define ABS_THROTTLE 0x06
#define ABS_RUDDER 0x07
/* 类似的 还有 Misc events LEDs etc.*/
|
value
键值,与事件类型以及键码有关,如果是按键事件,键码确定哪个按键,键值确定是按下还是抬起;如果是绝对事件,键码确定是哪个坐标轴,键值确定值是多少。
在Linux内核中,input设备用input_dev结构体描述,定义在input.h中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| /* include/linux/input.h */
struct input_dev {
const char *name;
const char *phys;
const char *uniq;
struct input_id id;
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)];
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
unsigned int keycodemax;
unsigned int keycodesize;
void *keycode;
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, int scancode, int keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, int scancode, int *keycode);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key;
struct timer_list timer;
int sync;
int abs[ABS_MAX + 1];
int rep[REP_MAX + 1];
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
int absmax[ABS_MAX + 1];
int absmin[ABS_MAX + 1];
int absfuzz[ABS_MAX + 1];
int absflat[ABS_MAX + 1];
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
struct input_handle *grab;
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
int going_away;
struct device dev;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};
|
注意: 一般不直接填充该结构,一个位表示一种功能,通常采用set_bit()函数间接填充。
例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| /* 1. 动态分配核心数据结构*/
struct input_dev * My_input_dev = input_allocate_device();
/* 2. 填充事件 */
// 按键事件
set_bit(EV_KEY, My_input_dev->evbit);
// 字母Q键
set_bit(KEY_Q, My_input_dev->keybit);
/* 3. 向内核注册一个input_dev */
input_register_device(My_input_dev);
/* 4. 在MODULE_EXIT中释放核心数据结构 */
input_unregister_device(My_input_dev);
input_free_device(My_input_dev);
/* 5. 在中断服务函数中 上报事件 */
input_report_key(My_input_dev, code, value);
/*
此外还有类似的 input_report_rel() , input_report_abs()等函数。
*/
input_sync(My_input_dev);
/* 6. 在应用程序中接收事件 */
fd = open("/dev/input/event1", O_RDWR);
read(fd, &My_event, siezeof(My_event));
switch(My_event.type) {
case EV_KEY:
switch(My_event.code) {
case KEY_Q:
...
}
}
|
编程实例
一个简单的按键驱动实例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
| /* simple_input_btn.c */
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
struct input_dev *btn_input;
static int irqno ;
irqreturn_t button_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
printk("--------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 获取数据
int value = gpio_get_value(S5PV210_GPH0(1));
if(value)
{
//抬起
//将数据上报给用户
//参数1---哪个设备上报的
//参数2---上报那种数据类型
//参数3---上报码值
//参数4--按键的状态/值
//input_report_key(btn_input, KEY_DOWN, 0);
input_event(btn_input, EV_KEY, KEY_DOWN, 0);
//最后要有一个结束/同步
input_sync(btn_input);
}else{
//按下
input_event(btn_input, EV_KEY, KEY_DOWN, 1);
input_sync(btn_input);
}
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int __init simple_btn_input_init(void)
{
int ret;
/*
a, 分配一个input device对象
b, 初始化input device对象
c, 注册input device对象
d, 硬件初始化
*/
//a, 分配一个input device对象
btn_input = input_allocate_device();
if(btn_input == NULL)
{
printk("input_allocate_device error\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
//b, 初始化input device对象
//该设备能够产生哪种数据类型---EV_KEY表示产生按键数据
//btn_input->evbit[0] |= BIT_MASK(EV_KEY);
set_bit(EV_KEY, btn_input->evbit);
//能够产生哪个按键---比如能够产生下键 KEY_DOWN, KEY_ESC
// btn_input->keybit[108/32] |= 1<<(108%32);
// btn_input->keybit[BIT_WORD(KEY_DOWN)] |= BIT_MASK(KEY_DOWN);
set_bit(KEY_DOWN, btn_input->keybit);
//c, 注册input device对象
ret = input_register_device(btn_input);
if(ret != 0)
{
printk("input_register_device error\n");
goto err_free_input;
}
//d, 硬件初始化--申请中断
irqno = IRQ_EINT(1);
ret = request_irq(irqno, button_interrupt, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING|IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING,
"key_input_eint1", NULL);
if(ret != 0)
{
printk("request_irq error\n");
goto err_unregister;
}
return 0;
err_unregister:
input_unregister_device(btn_input);
err_free_input:
input_free_device(btn_input);
return ret;
}
static void __exit simple_btn_input_exit(void)
{
free_irq(irqno, NULL);
input_unregister_device(btn_input);
input_free_device(btn_input);
}
module_init(simple_btn_input_init);
module_exit(simple_btn_input_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
|
对应的应用测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| #include <linux/input.h>
struct input_event key_event;
int main(int argc, char ** argv)
{
int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
while(1) {
read(fd, &key_event, siezeof(struct input_event));
switch(key_event.type) {
case EV_KEY:
switch(key_event.code) {
case KEY_DOWN:
if (key_event.value)
printf("key DOWN press\n");
else
printf("key DOWN release\n");
break;
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
