2019贝壳找房四道笔试题
1. 计算绝对值
题目描述:
给出n个正整数,要求将找出相邻两个数字中差的绝对值最小的一对数字,如果有差的绝对值相同的,则输出最前面的一对数。
输入:
输入包含两行,第一行为n,第二行是用空格分隔的n个正整数。
输出:
输出包含一行两个正整数,要求按照原来的顺序输出。
样例输入:
1
2
| 9
1 3 4 7 2 6 5 12 32
|
样例输出:
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin>>n;
int nums[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>nums[i];
int min_dif = abs(nums[1]-nums[0]);
int l = nums[0];
int r = nums[1];
for (int i=1; i<n; i++) {
int dif = abs(nums[i+1] - nums[i]);
if(dif < min_dif) {
l = nums[i];
r = nums[i+1];
min_dif = dif;
}
}
cout<<l<<" "<<r<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
2. 举重大赛
题目描述:
举重大赛开始了,为了保证公平,要求比赛的双方体重较小值要大于等于较大值的90%,那么对于这N个人最多能进行多少场比赛呢?任意两人之间醉倒进行一场比赛。
输入:
第一行:一个整数N,表示参赛人数(2<=N<=10^5)
第二行: N个正整数表示体重(0<体重<=10^8)
输出:
一个数,表示最多能进行的比赛场数
样例输入:
样例输出:
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin>>n;
int nums[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>nums[i];
int cnt = 0;
sort(nums, nums+n);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (int j=i+1; j<n; j++) {
if(nums[i]>= (double)(9.0/10)*nums[j])
cnt++;
else
break; //已经按照体重进行了排序,所以如果j不满足条件,那么后边的都不满足
}
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
3. 特殊的测试
题目描述:
小C在做一种特殊的服务器负载测试,对于一个请求队列中的请求,每一个请求都有一个负荷值,为了保证服务器稳定,请求队列中的请求负荷必须按照先递增后递减的规律(仅递增,仅递减也可以),比如[1,2,8,4,3]和[1,3,5]都是满足要求的。还有一些不满足的,比如[1,2,2,1]和[2,1,2]。现在给你一个请求队列,你可以对请求的负荷值进行增加,要求调整完的序列满足要求。
输入:
第一行是N(1<=N<=5000),代表请求队列中的请求数量。
第二行有N个整数Ai, Ai是第i个请求的负荷值。
输出:
输出这个最小增加总和。
样例输入:
样例输出:
样例说明:
1 5 3+2 2+4 5 一共增加了2+4=6。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin>>n;
int nums[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>nums[i];
vector<int> back(nums, nums+n);
if (n<2) {
return 0;
} else if (n==2) {
if(nums[0] == nums[1])
return 1;
else
return 0;
} else {
int i = 0;
while (i<n-1 && nums[i]<nums[i+1])
i++;
int j = n-1;
while (j>0 && nums[j]<nums[j-1])
j--;
while (i<j) {
if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i+1])
nums[i+1] = nums[i]+1;
i++;
} else {
if (nums[j] > nums[j-1])
nums[j-1] = nums[j]+1;
j--;
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
sum+=(nums[i]-back[i]);
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
4. 最长上升子序列
leetcode的第300道题目
题目描述:
给定一个无序的整数数组,找到其中最长上升子序列的长度。
输入: [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
输出: 4
解释: 最长的上升子序列是 [2,3,7,101],它的长度是 4。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin>>n;
int nums[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>nums[i];
int maxx = 0;
int dp[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j=0; j<i; j++) {
if (nums[j] < nums[i])
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
}
if (dp[i] > maxx)
maxx = dp[i];
}
cout<<maxx<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
图森笔试题
1. 求卷积

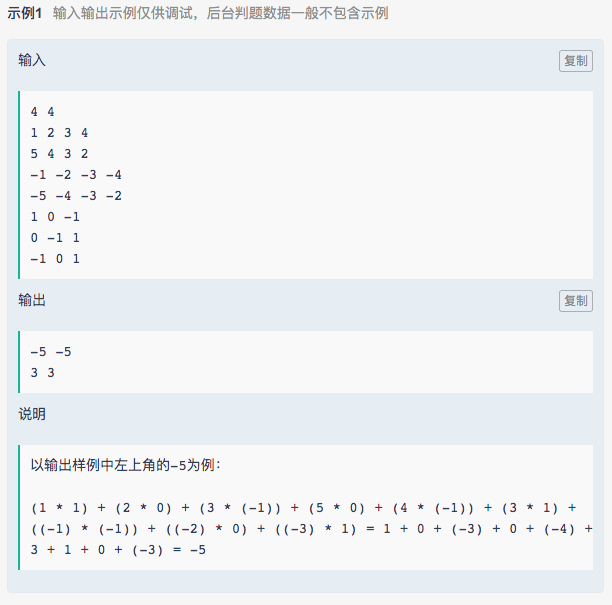
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int A[505][505];
int B[3][3];
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<m; j++) {
cin>>A[i][j];
}
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<3; j++) {
cin>>B[i][j];
}
}
vector<vector<int> > C(n-2, vector<int>(m-2));
for (int i=0; i<(n-2); i++) {
for (int j=0; j<(m-2); j++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int k=0; k<3; k++){
for (int l=0; l<3; l++) {
sum += A[i+k][j+l] * B[k][l];
}
}
C[i][j] = sum;
cout<<C[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
2. 迷宫求最短路径

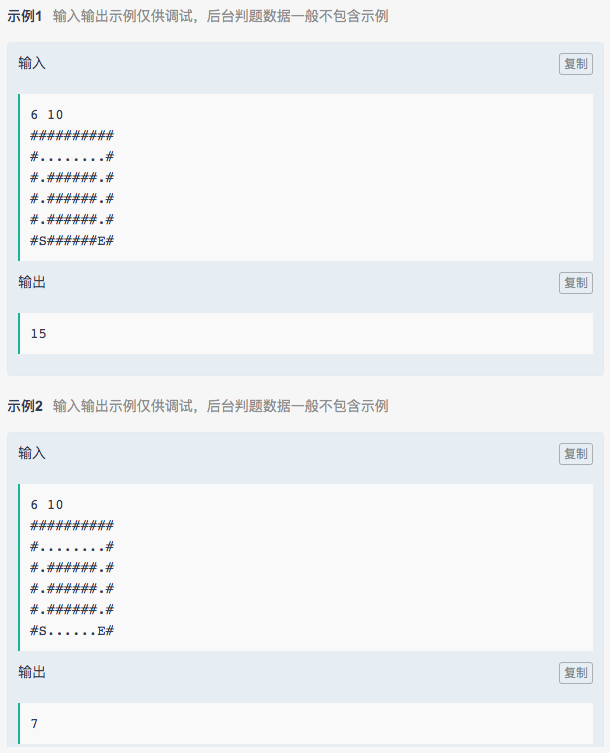
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| #include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 1005;
const int MAX_M = 1005;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
char maze[MAX_N][MAX_M + 1];
int N, M;
int sx, sy; //起点的位置
int gx, gy; //终点的位置
int d[MAX_N][MAX_M];//储存起点到某一点的距离
int dx[4] = { 1,0,-1,0 }, dy[4] = { 0,1,0,-1 }; //表明每次x和y方向的位移
void bfs()
{
queue<P> que;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++)
d[i][j] = INF; //初始化所有点的距离为INF
que.push(P(sx, sy));
d[sx][sy] = 0; //从起点出发将距离设为0,并放入队列首端
while (que.size()) //题目保证有路到终点,所以不用担心死循环
{
P p = que.front();
que.pop();//弹出队首元素
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = p.first + dx[i];
int ny = p.second + dy[i];//移动后的坐标
//判断可移动且没到过
if (0 <= nx && nx < N
&& 0 <= ny && ny < M
&& maze[nx][ny] != '#'
&& d[nx][ny] == INF)//之前到过的话不用考虑,因为距离在队列中递增,肯定不会获得更好的解
{
que.push(P(nx, ny)); //可以移动则设定距离为之前加一,放入队列
d[nx][ny] = d[p.first][p.second] + 1;
if(nx==gx && ny==gy)
break;
}
}
if(i!=4)
break;
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>N>>M;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++)
{
cin>>maze[i][j];
if (maze[i][j] == 'S')
{
sx = i; sy = j;
}
if (maze[i][j] == 'E')
{
gx = i; gy = j;
}
}
bfs();
cout<<d[gx][gy]<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
3. 我也不知道是什么题

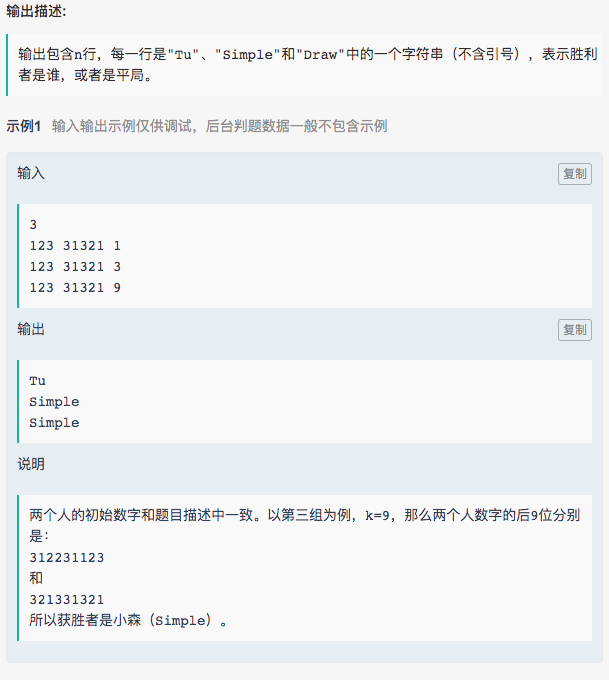
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string toStr(int x)
{
string ans;
while(x) {
ans.push_back(x%10+'0');
x /= 10;
}
return string(ans.rbegin(), ans.rend());
}
vector<char> tok(int x, int k)
{
string tt = toStr(x);
int len_t = tt.length();
vector<char> str_t;
int kk = k/len_t;
if (kk%len_t || kk==0)
kk+=1;
for (int i=kk-1;i>=0; i--) {
for (int j=i; j<len_t+i; j++) {
str_t.push_back( tt[j%len_t] );
}
}
return str_t;
}
string winer(int t, int s, int k)
{
vector<char> v_t = tok(t, k);
vector<char> s_t = tok(s, k);
int l_v_t = v_t.size()-k;
int l_v_s = s_t.size()-k;
int i;
for (i=0; i<k; i++) {
if (v_t[l_v_t+i] > s_t[l_v_s+i]) {
return "Tu";
} else if (v_t[l_v_t+i] < s_t[l_v_s+i]) {
return "Simple";
}
}
if (i==k)
return "Draw";
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
int t, s, k;
cin>>t>>s>>k;
cout<<winer(t, s, k)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
小米
1. 完全背包问题
n件商品,每件商品的价格固定,数量不限,固定的钱数,求最少拿走的商品数量。
2. 给定一个字符串表示的二叉树,输出中序遍历序列
输入样例:1(2(3,4(,5)),6(7,))
输出样例:3245176
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| string solution(string)
{
string res;
int len = input.length();
if (len == 0)
return res;
stack<char> st;
for (int i=0; i<len; i++) {
if (input[i] == '(' || input[i] ==')')
continue;
if (input[i]>='0' && input[i]<='9')
st.push(input[i]);
if (input[i] == ',') {
if (st.empty())
continue;
res.push_back(st.top());
st.pop();
if ((input[i-1]>='0' && input[i-1]<='9') || (input[i-1]==')')) {
if (st.empty())
continue;
res.push_back(st.top());
st.pop();
}
}
}
while (!st.empty()) {
res.push_back(st.top);
st.pop();
}
return res;
}
|
华为
1. 计算数轴上关系匹配的点
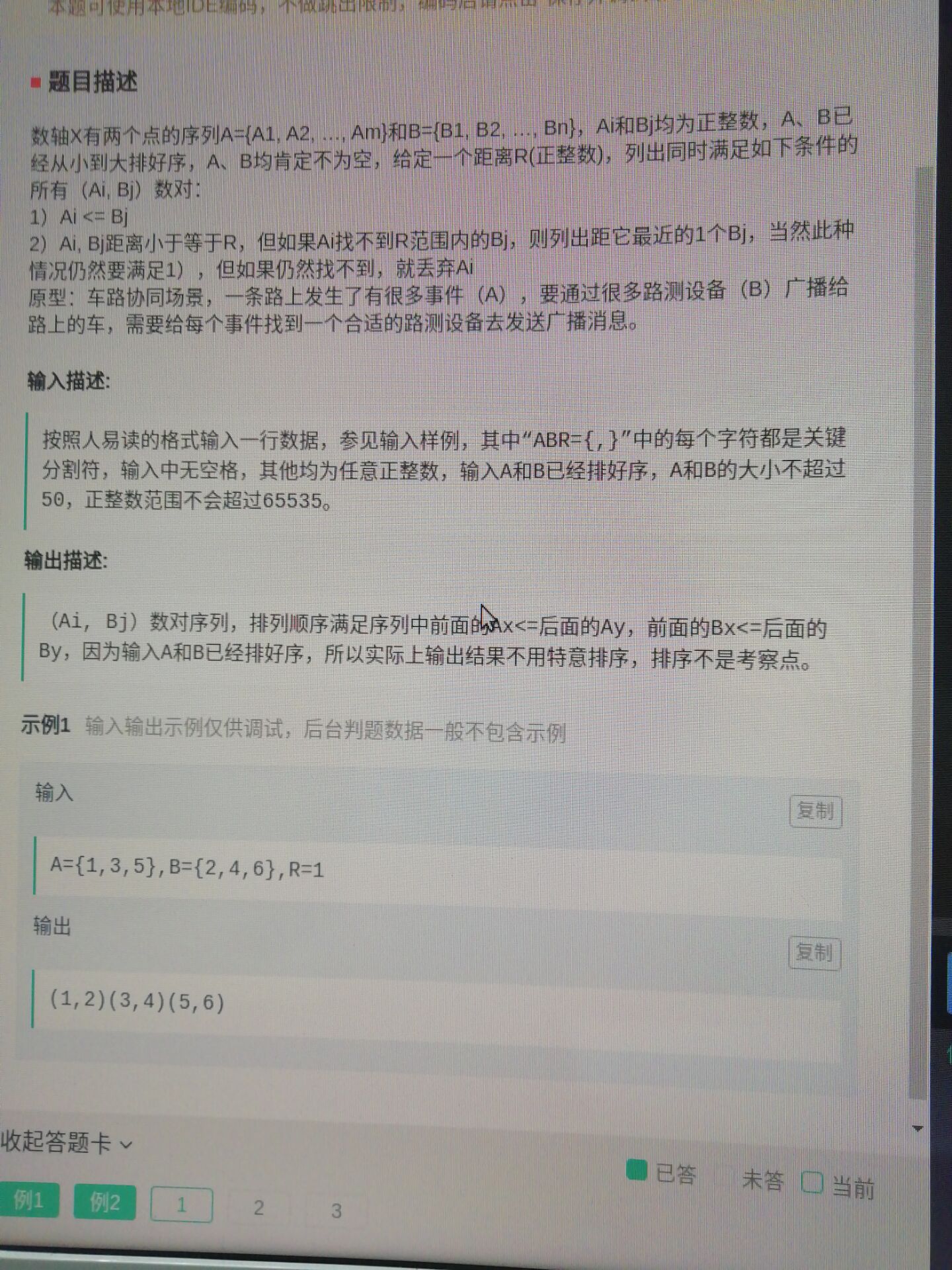
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int str2int(string str)
{
int res = 0;
for (auto it=str.begin(); it!=str.end(); it++) {
if (*it > '0' && *it < '9') {
int x = *it-'0';
res = res*10+x;
}
}
return res;
}
string int2str(int n)
{
string res;
while (n) {
int a = n%10;
res.push_back(a+'0');
n /= 10;
}
return string(res.rbegin(), res.rend());
}
string check(vector<int> A, vector<int> B, int R)
{
string res;
int len_a = A.size();
int len_b = B.size();
for (int i=0; i<len_a; i++)
{
if (A[i] > B[len_b-1])
break;
bool flag = false;
for (int j=0; j<len_b; j++) {
if (A[i] <= B[j]) {
if (B[j]-A[i] <= R) {
res += "(" +int2str(A[i]) + "," + int2str(B[j]) + ")";
flag = true;
}
}
}
if (!flag) {
int j = len_b-1;
while(B[j]>=A[i])
j--;
res += "(" + int2str(A[i]) + "," + int2str(B[j+1]) +")";
}
}
return res;
}
vector<int> str2vec(string str)
{
string tmp;
vector<int> vec;
for (auto it=str.begin(); it!=str.end(); it++) {
if (*it >= '0' && *it <= '9') {
tmp.push_back(*it);
} else if (*it == ',' || *it == '}') {
vec.push_back(str2int(tmp));
tmp = "";
}
}
return vec;
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int pos = s.find('R');
string R = s.substr(pos+2);
int r = str2int(R);
s = s.substr(0, pos-1);
pos = s.find("B");
string str_b = s.substr(pos+3);
vector<int> B = str2vec(str_b);
s = s.substr(0, pos-1);
string str_a = s.substr(3);
vector<int> A = str2vec(str_a);
cout<<check(A, B, r);
return 0;
}
|
2. 翻转字符串

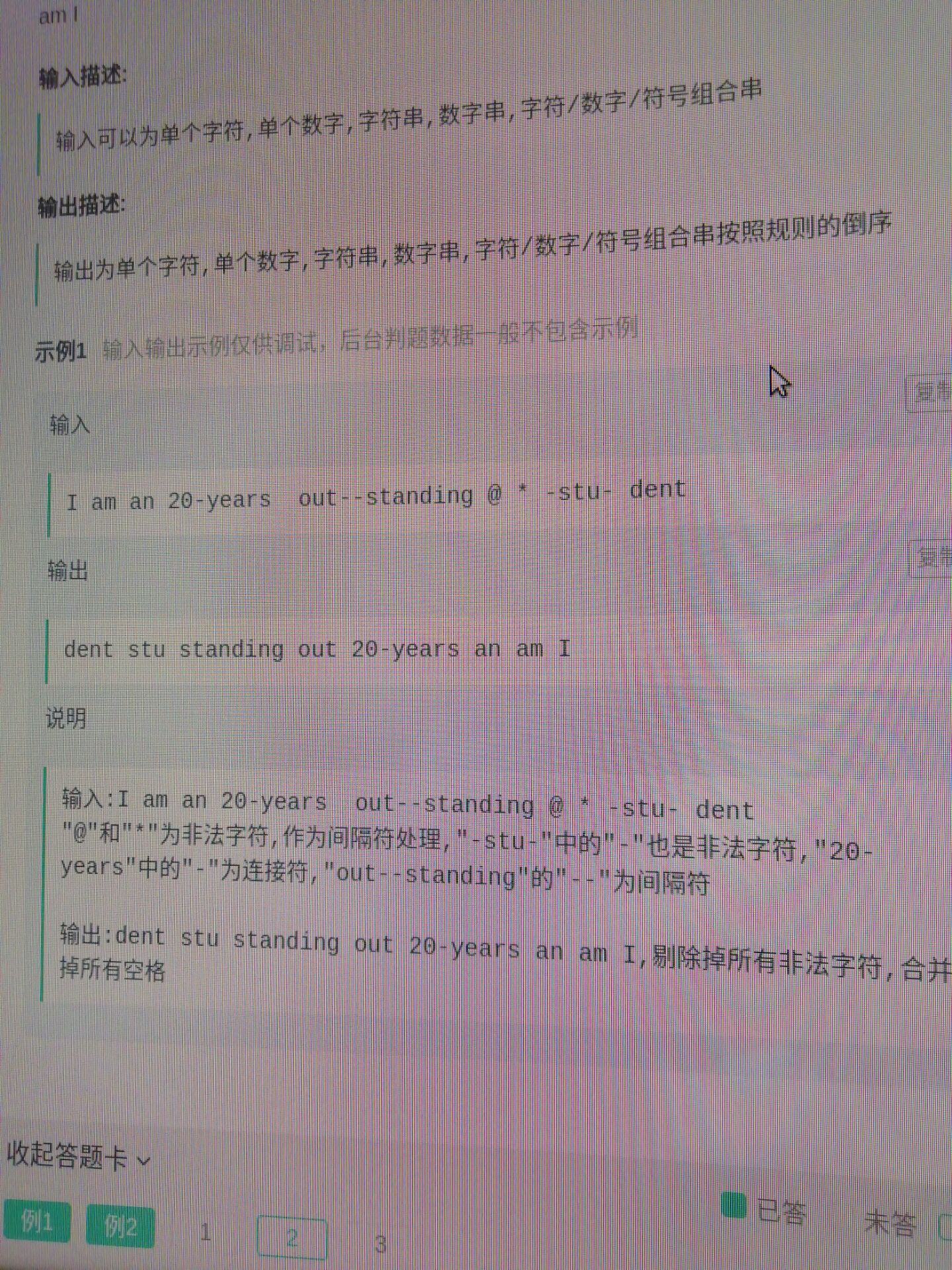
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define VALID(it) ((*(it)>='0' && *(it)<='9') || (*(it)>='a'&&*(it)<='z') || (*(it)>='A'&& *(it)<='Z') )
int main()
{
string str;
getline(cin, str);
string n_str;
for (auto it=str.begin(); it!=str.end(); it++) {
if ( VALID(it) ) {
n_str.push_back(*it);
} else {
if (*it == '-') {
if (VALID((it+1)) && VALID((it-1)) )
n_str.push_back(*it);
}
auto it = n_str.end();
if (*(it-1) != ' ')
n_str.push_back(' ');
}
}
int pos;
while((pos=n_str.rfind(' ')) != string::npos){
string ss = n_str.substr(pos+1);
cout<<ss<<" ";
n_str = n_str.substr(0, pos);
}
cout<<n_str<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
另一种方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| 1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3
4 static char buf[] = "I am an 20 ye-ars out--standing @ * -stu- dent";
5
6 int is_valid(char ch)
7 {
8 if (((ch>='a') && (ch<='z'))
9 || ((ch>='A') && (ch<='Z'))
10 || ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9'))) {
11 return 1;
12 }
13 else {
14 return 0;
15 }
16 }
17
18 int main(void)
19 {
20 char *pos = NULL;
21 int size = 0;
22 int i = 0;
23
24 size = strlen(buf) + 1;
25 printf("size: %d\n", size);
26
27 for (pos = buf + size - 2; pos != buf; pos--) {
28 if (!is_valid(*pos)) {
29 if ((*pos == '-')) {
30 if ((is_valid(*(pos-1))) && (is_valid(*(pos+1)))) {
31 continue;
32 }
33 else {
34 *pos = 0;
35 }
36 }
37 if (*(pos + 1) != '\0') {
38 printf("%s ", pos + 1);
39 }
40 *pos = 0;
41 }
42 }
43 printf("%s\n", buf);
44
45 return 0;
46 }
|
3. 修改机票信息
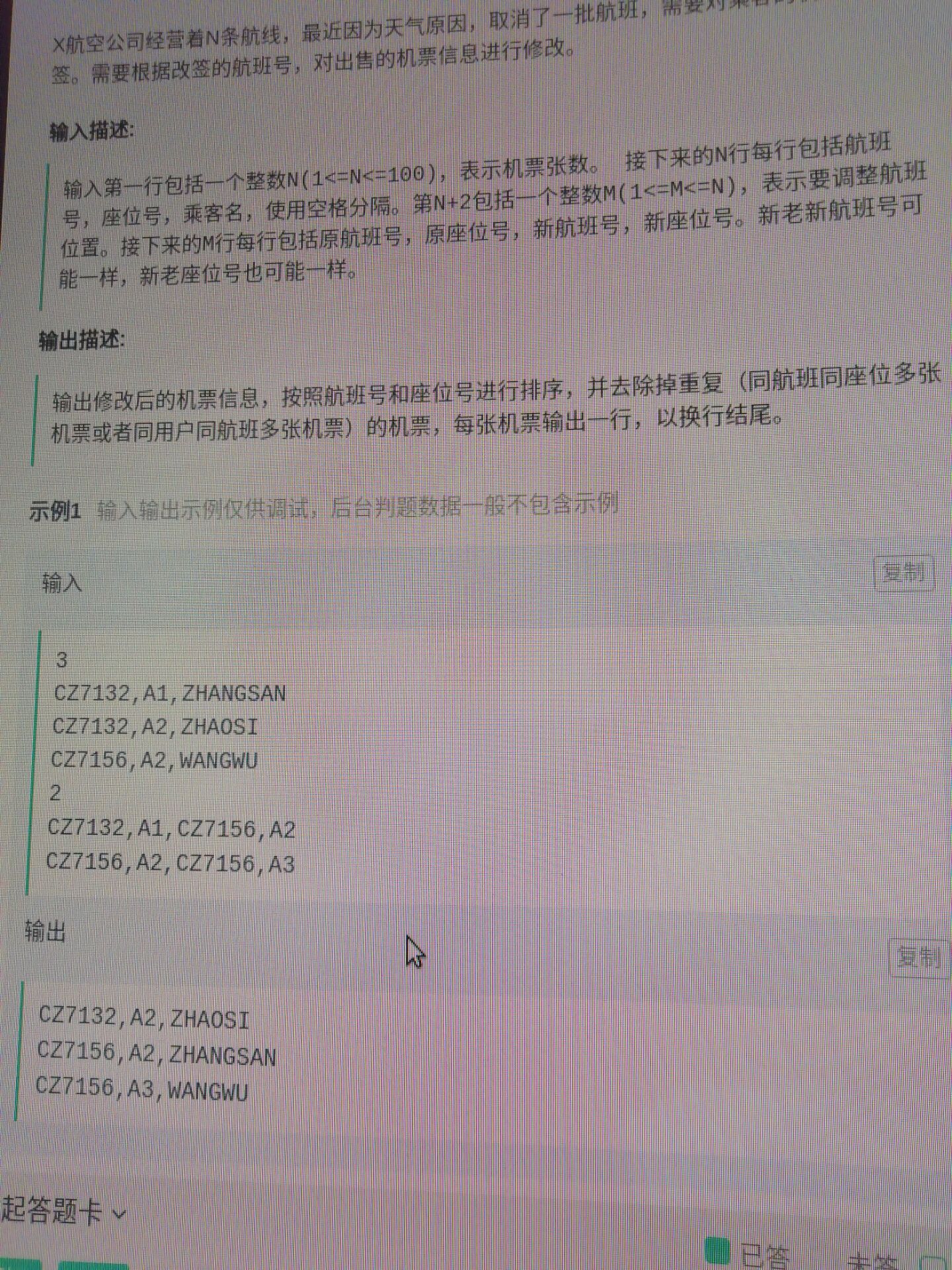
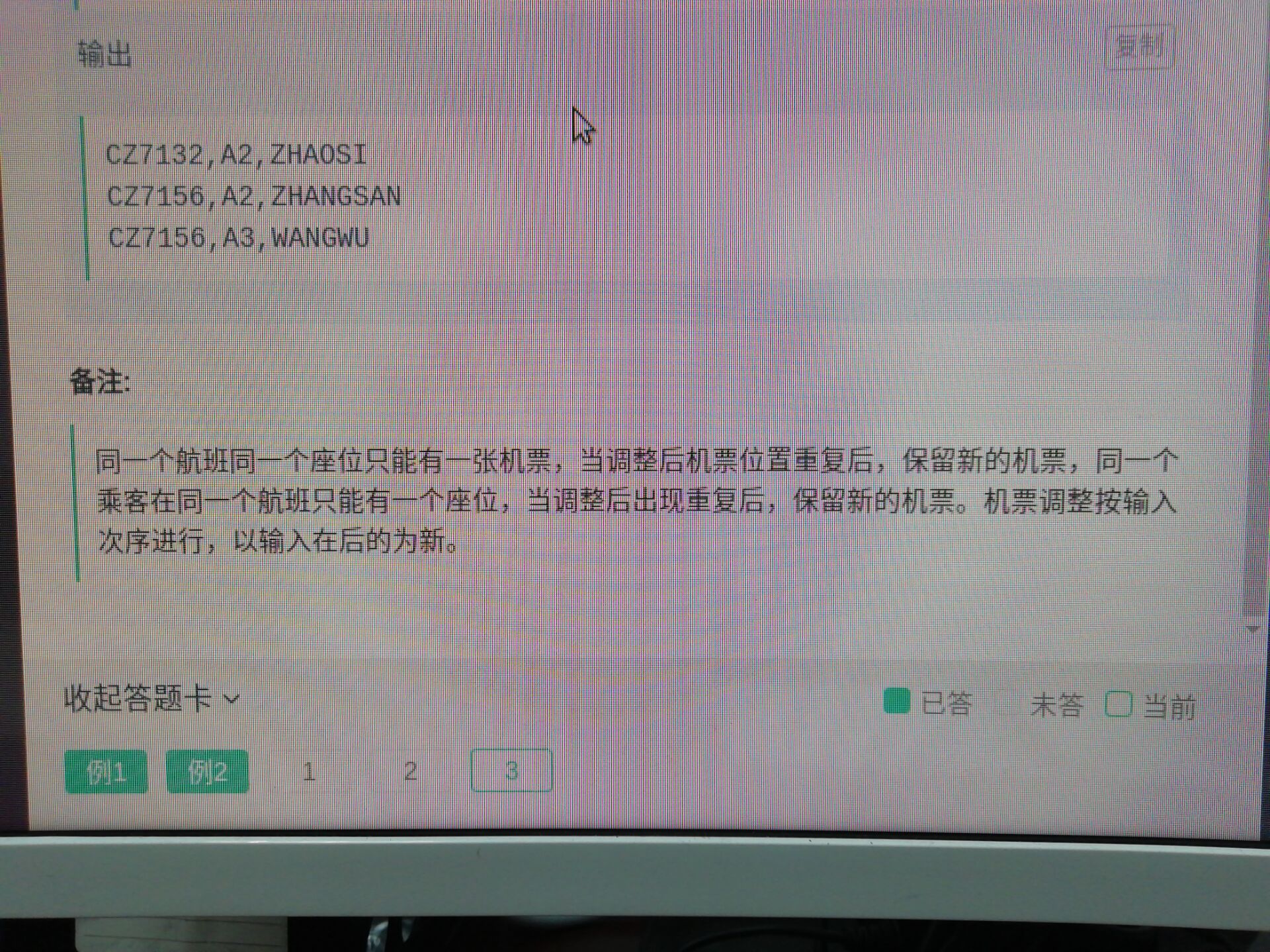
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct INFO{
string hbh;
string zwh;
string name;
bool rewrite;
INFO(string num_hb, string num_zw, string na)
{
this->hbh = num_hb;
this->zwh = num_zw;
this->name = na;
this->rewrite = false;
}
};
bool cmp(const INFO & a, const INFO & b)
{
if (a.hbh == b.hbh) {
return a.zwh<b.zwh;
} else {
return a.hbh<b.hbh;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin>>n;
vector<INFO> info;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
string hbh, zwh, name;
cin>>hbh>>zwh>>name;
INFO tmp(hbh, zwh, name);
info.push_back(tmp);
}
cin>>m;
for (int i=0; i<m; i++) {
string ohb, ozw, nhb, nzw;
cin>>ohb>>ozw>>nhb>>nzw;
for (int j=0; j<n; j++) {
if ((ohb == info[j].hbh) && (ozw == info[j].zwh) && !(info[j].rewrite)) {
info[j].hbh = nhb;
info[j].zwh = nzw;
info[j].rewrite = true;
}
}
}
sort(info.begin(), info.end(), cmp);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
cout<<info[i].hbh<<","<<info[i].zwh<<","<<info[i].name<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
总结
华为的题,总体感觉不难,和刷LeetCode的感觉是不一样的,leetcode注重算法。而华为的题感觉更加注重用代码实现逻辑功能。输入处理起来异常麻烦。
第一题没有A掉,很明显代码中的条件处理的也不够,但是过了百分之八十,我同学他们没有考虑数字是两位或者多位的情况也过了百分之八十,不知道怎么回事。
第二题A掉了。
第三题,没时间写完,后来写的没有处理机票重复的情况。
vivo
1.
2. 报数
N个人站成一个圈,从1开始报数到M的整数倍时出去一个人,问出去的人的序列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
/**
* Welcome to vivo !
*/
typedef struct _node
{
int num;
struct _node * next;
}node;
void solution(int N, int M)
{
// TODO Write your code here
node * head = NULL;
node * tail = NULL;
for (int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
node * p = new node;
p->num = i;
p->next = NULL;
if (head == NULL) {
head = p;
tail = p;
} else {
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
tail->next = head;
}
}
node * q = head;
int count = 1;
while (q!=NULL && q!=q->next) {
if (count % M == 0) {
cout<<q->num<<" ";
node * qq = q->next;
q->num = qq->num;
q->next = qq->next;
delete qq;
} else {
q=q->next;
}
count++;
}
if (q!=NULL)
cout<<q->num<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int N;
int M;
string str("");
getline(cin, str);
char *p;
const char* strs = str.c_str();
p = strtok((char *)strs, " ");
N = atoi(p);
p = strtok(NULL, " ");
M = atoi(p);
solution(N, M);
return 0;
}
|
3. 天平问题
类似与这道题










